2024年机器人与自动化国际会议(ICRA 2024)于5月13日至5月17日在日本横滨举行。上海交通大学智能网联电动汽车创新中心(以下简称“中心”)师生在本次会议上发表的论文简介如下:
01
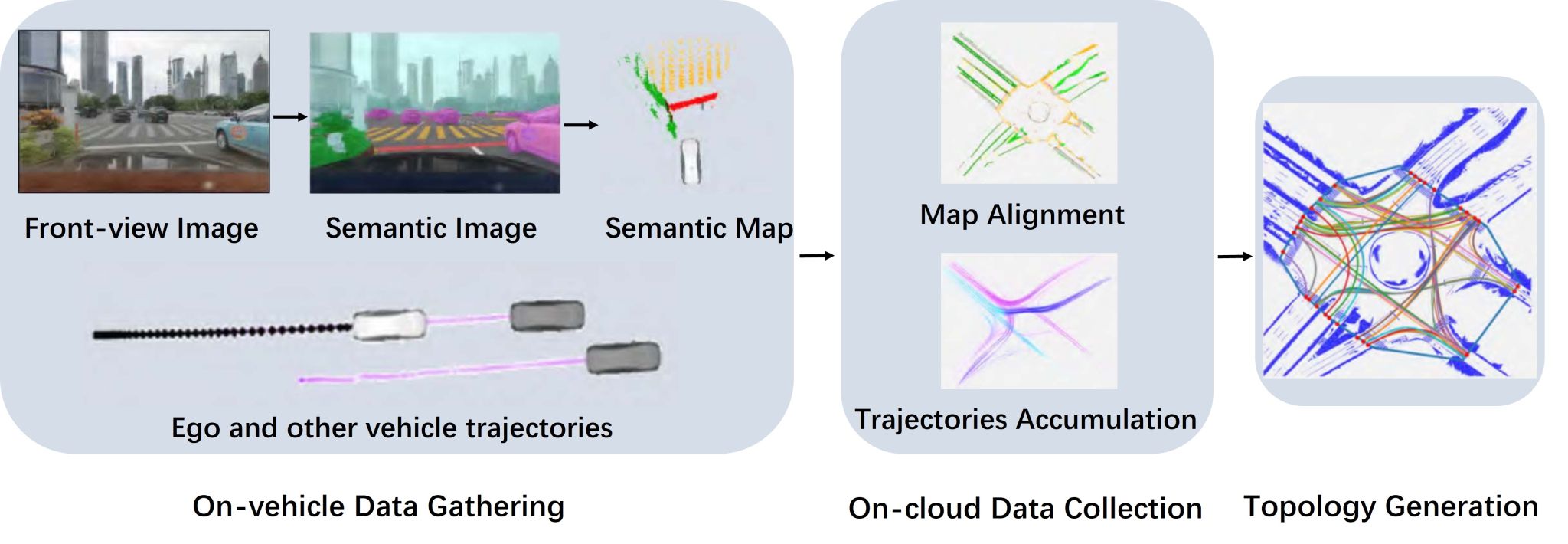
Traffic Flow-Based Crowdsourced Mapping in Complex Urban Scenario
Tong QIN , Haihui HUANG , Ziqiang WANG , Tongqing CHEN , Wenchao DING
An accurate road topological structure is of great importance for autonomous driving in complex urban environments. Currently, most autonomous vehicles highly rely on the High-Definition map (HD map) to cruise across the city. Without the prior map, it's hard for vehicles to find right-turning and left-turning ways in large intersections. However, due to the complexity of intersections, producing such a map by human resources is time-consuming and error-prone. In this paper, we proposed a framework to automatically produce the topological map of complicated intersections. This framework adopts the crowdsourcing way to collect semantic information about the environment and traffic flows. The topological structure is inferred from traffic flows correctly and automatically. We highlight that this framework is highly automatic and scalable, which can greatly speed up HD map production and decrease the cost. The proposed system is validated by real-world crowdsourcing data and the result is comparable to the traditional HD maps.
02
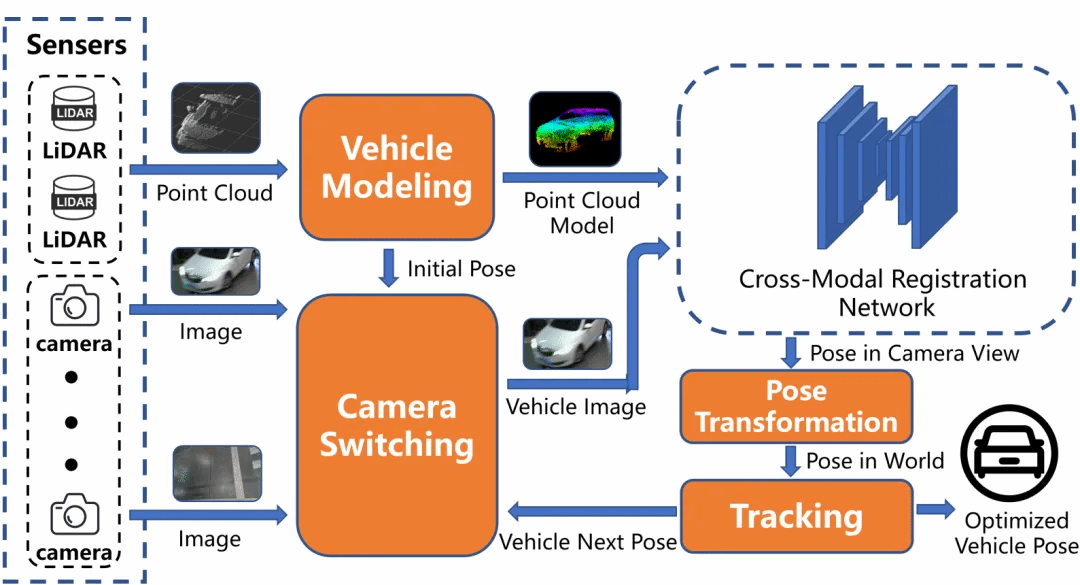
Cross-Modal Registration Using Adaptive Modeling in Infrastructure-Based Vehicle Localization
Fei WANG , Yuesheng HE , Hanyang ZHUANG , Chenxi YANG , Ming YANG
Infrastructure-based vehicle localization, in comparison to single-agent approaches, offers several advantages including reduced system cost, extended perception range, enhanced data fusion capabilities, and energy savings. Many conventional approaches impose limitations on the types of objects due to the need for specific object-end modifications, such as applying perceptual markers like color-labeled plates and reflective balls. LiDAR presents a solution in terms of object arbitrariness, as it addresses the challenges of feature-free object modeling and continuous registration. However, achieving complete environmental coverage with LiDAR remains prohibitively expensive, particularly in extensive areas. Hence, this study proposes a cross-modal localization approach using adaptive modeling, employing LiDAR for object modeling and cost-effective sensor cameras for object tracking through image-point-cloud registration. Accurate correspondence between the model and observation can be estimated in real-time. The experiments are conducted in a typical scenario that requires adaptive modeling: Autonomous Valet Parking (AVP). Results demonstrate that the proposed system achieves comparable performance with significantly reduced system costs, highlighting its potential for large-scale deployment.
03
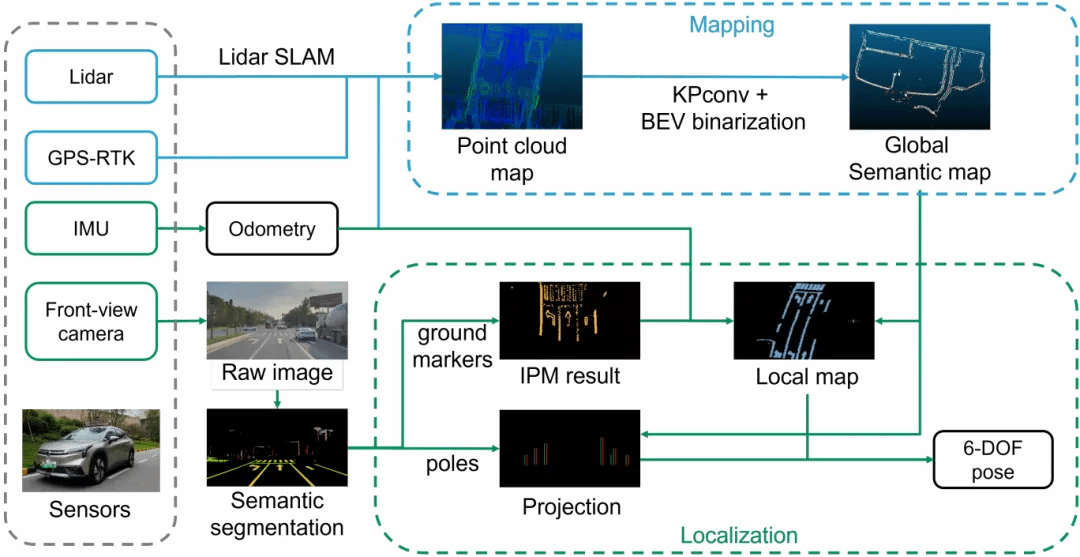
Monocular Localization with Semantics Map for Autonomous Vehicles
Jixiang WAN , Xudong ZHANG , Shuzhou DONG , Yuwei ZHANG , Yuchen YANG , Ruoxi WU , Ye JIANG , Jijunnan LI , Jinquan LIN , Ming YANG
Accurate and robust localization remains a significant challenge for autonomous vehicles. The cost of sensors and limitations in local computational efficiency make it difficult to scale to large commercial applications. Traditional vision-based approaches focus on texture features that are susceptible to changes in lighting, season, perspective, and appearance. Additionally, the large storage size of maps with descriptors and complex optimization processes hinder system performance. To balance efficiency and accuracy, we propose a novel lightweight visual semantic localization algorithm that employs stable semantic features instead of low-level texture features. First, semantic maps are constructed offline by detecting semantic objects, such as ground markers, lane lines, and poles, using cameras or LiDAR sensors. Then, online visual localization is performed through data association of semantic features and map objects. We evaluated our proposed localization framework in the publicly available KAIST Urban dataset and in scenarios recorded by ourselves. The experimental results demonstrate that our method is a reliable and practical localization solution in various autonomous driving localization tasks.
ICRA是机器人领域规模(千人以上)和影响力均排名第一的顶级国际会议,是机器人领域权威研究人员介绍其研究成果的首要国际论坛。ICRA 2024共收到来自58个国家的3937篇投稿,经过由28个编辑、588个副编辑和6719个审稿人的评审,其中1765篇被录用。
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ntVPcAi0_5jorFwME_82Cg
